Giới Thiệu Về API Là Gì?
22/04/2022
1.64k

Xin chào các bạn, mình là Thắng, thành viên team QC của SupremeTech. Trong bài viết này, mình sẽ giải thích cho các bạn về một khái niệm rất quen thuộc trong kiểm thử nói riêng mà còn trong ngành IT nói chung, đó là API.
Mình nhớ khoảng thời gian đầu tiên khi mình bắt đầu nhận việc trong một dự án với yêu cầu chỉ có API; lúc đó mình còn chưa có đủ kiến thức và kinh nghiệm cùng với sự tự tin về mảng này. Có rất nhiều câu hỏi trong đầu mình như phải tìm hiểu thế nào? Kiểm thử ra sao? Và sau đó mình đã cố gắng học hỏi và thực hành rất nhiều, sau cùng mình nhận ra API không quá khó như lúc đầu mình nghĩ, ít nhất mình đã có được kinh nghiệm và kiến thức để tự tin áp dụng vào trong dự án.
Ở đây, mình sẽ chia sẻ lại cho các bạn những gì mình đã tìm hiểu, đã áp dụng vào thực tế, để mọi người có góc nhìn khác khi một tester nhìn vào API thì sẽ như thế nào nhé.
API là gì?
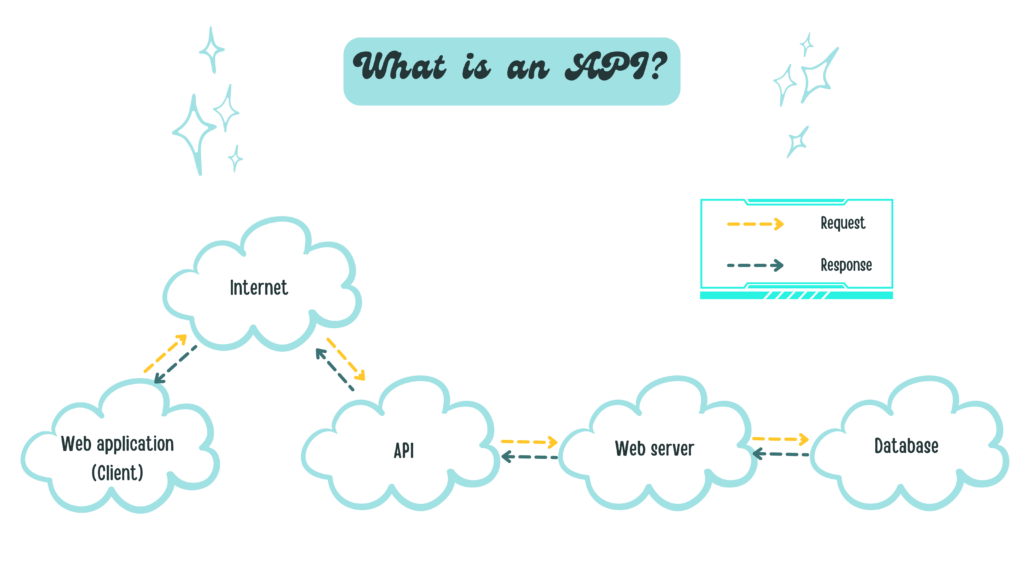
API là viết tắt của cụm từ Giao diện lập trình ứng dụng (Application Programming Interface). API cung cấp khả năng truy xuất đến một tập các hàm hay dùng. Và từ đó có thể trao đổi dữ liệu giữa các ứng dụng. Một cách dễ hiểu thì API là một trung gian phần mềm cho phép hai ứng dụng giao tiếp với nhau.
Ví dụ về API trong thực tế
Tưởng tượng bạn bước vào một nhà hàng, bạn đặt món, nhân viên phục vụ sẽ tiếp nhận yêu cầu của bạn và đưa vào nhà bếp, sau đó sẽ mang ra món ăn đúng với yêu cầu của bạn. Trong ví dụ trên, API là nhân viên phục vụ, đã giúp bạn và đầu bếp giao tiếp với nhau.
Bây giờ hãy nghĩ về một trường hợp ứng dụng API trong thực tế nhé. Giả sử bạn đi du lịch, bạn sẽ vào trang web của các hãng hàng không nhằm kiểm tra chuyến bay, giá cả, số ghế,… Nhưng vấn đề ở đây là có quá nhiều hãng hàng không và bạn lại không muốn mất thời gian cho những việc thế này, thay vào đó, bạn có thể sử dụng các dịch vụ trực tuyến trung gian nhiều tiện ích như Traveloka hay Expedia. Những dịch vụ đó sẽ tương tác với API của các hãng hàng không để hiển thị cho bạn các thông tin liên quan không chỉ của một mà còn của nhiều hãng bay khác nhau, từ đó giúp cho bạn tiết kiệm được rất nhiều gian và công sức. API thật tuyệt vời đúng không!
HTML là gì?
Khoảng thời gian sau khi World Wide Web (WWW) được ra đời vào cuối những năm 1980, nhu cầu trao đổi dữ liệu giữa các thiết bị điện tử trở nên phát triển hơn bao giờ hết. Vào thời điểm đó, các tập tin siêu văn bản HTML được đưa lên web và người sử dụng có thể đọc được nội dung một cách dễ dàng.
HTML là viết tắt của từ HyperText Markup Language – Ngôn ngữ Đánh dấu Siêu văn bản. Đây là một loại ngôn ngữ nhằm định dạng trang web thông qua các thẻ (tag) nhằm giúp cho máy tính hiểu được bố cục và cấu trúc của trang web và hiển thị trang web đó. Tuy nhiên lập trình viên chỉ có thể sử dụng những tag được quy định sẵn trong HTML khiến cho việc mở rộng hay tạo ra những nội dung mới trên website khá khó khăn.
Một vấn đề khác nữa là HTML chỉ đơn thuần là ngôn ngữ trình bày nội dung, nó không có chức năng lưu trữ hay trao đổi dữ liệu giữa các máy tính với nhau, nghĩa là các hệ thống không thể tương tác với nhau như cập nhật giá cả hàng ngày chẳng hạn.
XML là gì?
Do đó XML – Extensible Markup Language được ra đời với sứ mệnh tạo ra các tài liệu web cho cả người và máy tính đều có thể dễ dàng đọc được, khiến Internet thực sự trở thành một mạng lưới liên kết đúng nghĩa thật sự. XML được phát triển bởi mười một người đóng góp tại W3C vào năm 1997.
XML, đúng như tên gọi của nó (Extensible – mở rộng), đã giải quyết được một vài vấn đề của HTML như thay vì sử dụng các tag có sẵn thì XML cho phép các lập trình viên tự tạo ra các tag của chính mình, từ đó cho phép họ thể hiện được nhiều nội dung hơn trên website, và đặc biệt là XML cho phép gói dữ liệu vào trong nội dung văn bản và trao đổi giữa các hệ thống với nhau.
Trước khi XML ra đời thì các hệ thống vẫn có thể trao đổi dữ liệu với nhau nhưng đó là một quy trình rất phức tạp và phải thống nhất rất nhiều quy tắc, dẫn tới việc nếu trao đổi dữ liệu lớn thì sẽ xảy ra tình trạng bị mất dữ liệu trong lúc chuyển đổi. Với XML, lập trình viên có thể khai báo trước các tag của mình và các hệ thống đều có thể đọc được và tương tác với nhau dễ dàng hơn.
Mình sẽ lấy một ví dụ đơn giản cho bạn dễ hiểu nhé. Trong HTML có một thẻ tag là <title> nhằm khai báo tiêu đề trang web. Cấu trúc sẽ như thế này:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Supremetech blog</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Trong khi đó, với XML bạn có thể tự khai báo thẻ tag <title> với nhiều mục đích khác nhau như tiêu đề trang web và tiêu đề một quyển sách hiển thị trên trang web đó mà không lo bị lỗi:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<page>
<head>
<title>Book store</title>
</head>
<body>
<library>
<book>
<title>Harry Potter</title>
<author>J.K Rowling</author>
</book>
<book>
<title>Sherlock Holmes</title>
<author>Conan Doyle</author>
</book>
</library>
</body>
</page>
Các bạn có thể thấy thẻ tag <title> nằm trong thẻ <head> sẽ được máy tính hiểu là tiêu đề của trang, còn thẻ <title> nằm trong thẻ <book> sẽ được hiểu là tiêu đề của quyển sách.
SOAP và RESTful
Sau khi hiểu được API là gì, các bạn sẽ thấy API vô cùng quan trọng trong thời đại số như hiện nay. Và như một điều hiển nhiên, mọi thứ sau khi phát triển một thời gian sẽ hình thành những quy tắc chung. Sau đây mình sẽ giới thiệu 2 chuẩn phổ biến là SOAP là RESTful.
SOAP
Sau khi XML ra đời, một vài kỹ sư tại Microsoft đã phát triển SOAP. SOAP là một tiêu chuẩn dựa hoàn toàn vào XML để chuẩn hóa việc giao tiếp giữa server và thiết bị (client), từ đó giúp cho việc phát triển API tốt hơn. Sau khi SOAP xuất hiện, đặc biệt vào năm 2000, SOAP đã được Microsoft và IBM thúc đẩy và trở nên phổ biến. Một số công ty và các tập đoàn lớn đã sử dụng SOAP như HP hay Oracle cho các chương trình của họ.
Một vấn đề khá lớn của SOAP là có quá nhiều quy tắc phải tuân thủ khiến cho lập trình viên thấy nó quá khó để sử dụng. Mặc dù việc có nhiều quy tắc cũng là một ưu điểm của SOAP bởi vì nhờ đó các lập trình viên có thể tạo ra các hệ thống độc lập nhưng vẫn giao tiếp tốt với nhau. Từ khả năng giao tiếp tốt đó, các hệ thống lớn gồm nhiều hệ thống liên quan sẽ được quản lý và phát triển một cách dễ dàng hơn.
RESTful
Một nhà khoa học máy tính tên Roy Fielding đã nhìn ra vấn đề đó và giới thiệu tiêu chuẩn REST trong luận văn tiến sĩ của mình với mục đích duy nhất: tạo ra tiêu chuẩn giúp cho các server đều có thể giao tiếp được với nhau. Nếu như SOAP sử dụng XML để tạo request và response thì RESTful có thể tạo request với một URL đơn giản đi cùng với các phương thức (method) như GET, POST, PUT, DELETE và response trả về cũng được viết ở nhiều dạng như JSON hay CSV. Bạn hãy nhìn vào ví dụ dưới đây về request và response của API dùng để xem giá cả nếu được viết dưới dạng XML theo tiêu chuẩn SOAP:
- Request
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope/"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body>
<m:GetPrice xmlns:m="https://www.w3schools.com/prices">
<m:Item>Apples</m:Item>
</m:GetPrice>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
- Response:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope/"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body>
<m:GetPriceResponse xmlns:m="https://www.w3schools.com/prices">
<m:Price>1.90</m:Price>
</m:GetPriceResponse>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
Source: W3C
Rất là rắc rối và phức tạp đúng không nào. Trong khi đó nếu ta cũng dùng API gọi thông tin về giá sản phẩm theo RESTful thì chỉ cần gửi request tới URL (https://www.w3schools.com/prices), chọn method là GET thì sẽ có response dưới dạng JSON như sau:
{
"Apple": "1.90"
}
Nhìn vào API theo tiêu chuẩn RESTful bạn cũng nhận ra nó đơn giản và dễ dùng hơn SOAP đúng không? Đó là lí do mà vì sao RESTful được sử dụng rất nhiều vào ngày nay.
Một lí do khác là vào thời điểm những năm 2000, Internet phát triển cực kì mạnh mẽ, đặc biệt là mảng thương mại điện tử. Rất nhiều tập đoàn lớn lúc đó đã phát triển API của mình để nhiều bên có thể truy cập vào dữ liệu sản phẩm của họ. Lúc đó Salesforce là một trong những người tiên phong cung cấp API của mình dưới tiêu chuẩn SOAP nhưng lại không được nhiều lập trình viên ưa chuộng vì tài liệu hướng dẫn sử dụng hơn 400 trang.
Trong khi đó, Ebay, mặt khác lại cung cấp API theo chuẩn RESTful và đã đạt được sự thành công đáng kể so với đối thủ là Salesforce lúc bấy giờ khi mà nhiều bên cảm thấy API theo chuẩn RESTful dễ truy cập và dễ sử dụng. Kể từ đó là thời kì phát triển mạnh mẽ của RESTful API, nhiều ông lớn đã đi theo Ebay như Amazon, Flickr,… Dưới đây là sơ đồ thống kê mức độ phổ biến các chuẩn API vào năm 2014:
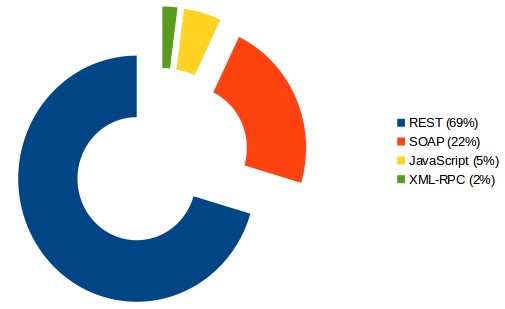
Dưới góc độ kiểm thử và sự phổ biến của RESTful nên mình sẽ nói kỹ hơn về chuẩn này nhé.
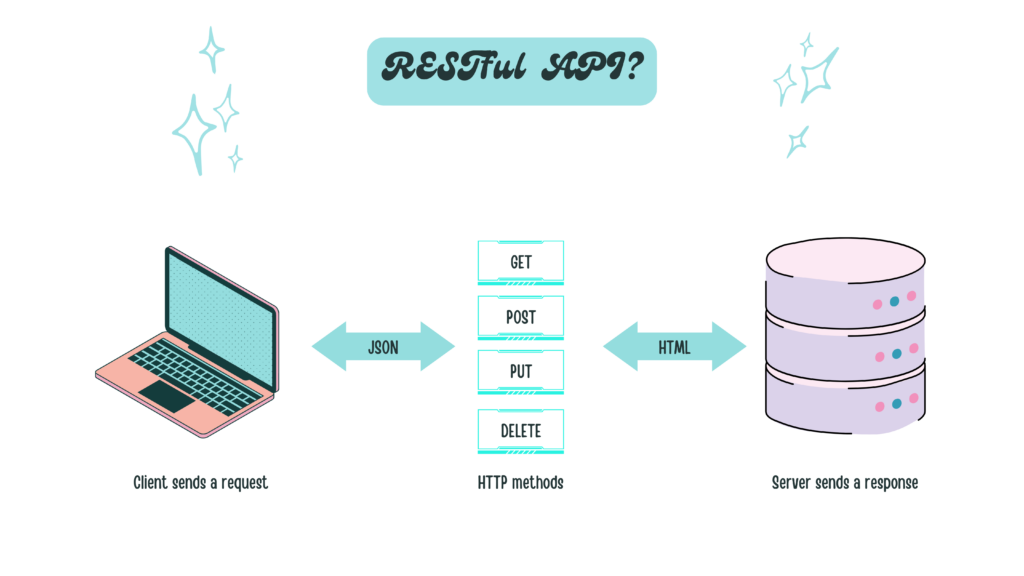
Hình ví dụ ở trên minh họa một cách đơn giản về nguyên lý hoạt động của API theo tiêu chuẩn RESTful. Hãy lấy lại ví dụ ở phần trước đó về việc bạn sử dụng Traveloka để xem thông tin về chuyến bay nhé. Bạn vào mục tra cứu chuyến bay trên web Traveloka, sau bước này thì website – client sẽ gửi request theo giao thức HTTP tới server của hãng bay. Tùy thuộc vào phương thức – method bạn gửi thì server sẽ có những xử lý tương ứng. Trong RESTful sẽ có 4 phương thức cơ bản sau đây:
- GET (SELECT): Trả về một Resource hoặc một danh sách Resource.
- POST (CREATE): Tạo mới một Resource.
- PUT (UPDATE): Cập nhật thông tin cho Resource.
- DELETE (DELETE): Xoá một Resource.
Những phương thức hay hoạt động này thường được gọi là CRUD tương ứng với Create – Tạo, Read – Đọc, Update – Sửa, Delete – Xóa.
Ví dụ ở đây bạn muốn xem thông tin về chuyến bay thì method client dùng sẽ là GET nhằm lấy về danh sách các chuyến bay theo yêu cầu của bạn. Sau khi server nhận được request của Client sẽ tiến hành trả về dữ liệu phù hợp response. Dữ liệu trả về thường được viết dưới dạng JSON hoặc XML tùy thuộc vào tính chất của dự án. Dữ liệu trả về gồm có cấu trúc như sau (mình sẽ để dưới dạng JSON nhé):
{
"status_code": 200,
"data": [
{
"name": "LH370",
"Time": "Mar 29, 2022",
"City": "DNG"
},
{
"name": "LH370",
"Time": "Mar 29, 2022",
"City": "HCM"
}
],
}
Các bạn có thể thấy ở response có dòng “status_code”, biến này sẽ cho chúng ta biết được trạng thái của response trả về. Các mã sẽ được phân thành các nhóm như sau:
- 2xx: Successful responses / Phản hồi thành công:
- 200 OK – Trả về thành công cho những phương thức GET, PUT, PATCH hoặc DELETE.
- 201 Created – Trả về khi một Resource vừa được tạo thành công.
- 204 No Content – Trả về khi Resource xoá thành công.
- 3xx: Redirects / Điều hướng
- 304 Not Modified – Client có thể sử dụng dữ liệu cache.
- 4xx: Client errors / Lỗi phía client
- 400 Bad Request – Request không hợp lệ
- 401 Unauthorized – Request cần có auth.
- 403 Forbidden – bị từ chối không cho phép.
- 404 Not Found – Không tìm thấy resource từ URL
- 5xx: Server errors / Lỗi phía máy chủ
- 500 Server Error: domain, hosting hết hạn, hoặc dừng server đột ngột để test
- 502 Bad Gateway
- 503 Service Unavailable
Web services là gì? Phân biệt API và web services
Và lúc này khái niệm web services trở nên phổ biến. Giờ chúng ta tìm hiểu thêm một khái niệm mới nhé.
Nói một cách khái quát, web services là những tài nguyên có sẵn trên internet, là dịch vụ cung cấp một số chức năng mà các ứng dụng khác có thể sử dụng. Chức năng này có thể bao gồm xử lý thanh toán, đăng nhập và lưu trữ cơ sở dữ liệu. Cả API và web services đều đóng vai trò giúp cho các ứng dụng giao tiếp được với nhau. Điểm khác biệt cơ bản giữa API và web services đó là web services giúp các ứng dụng giao tiếp với nhau trên Internet nhưng API có thể giúp các ứng dụng giao tiếp với nhau mà không cần Internet. Chúng ta có thể nói tất cả web services là API nhưng không phải API nào cũng là web services.
Hơi rắc rối đúng không nào, mình sẽ lấy một ví dụ cho bạn dễ hình dung nhé:
Hầu như trong cuộc sống ngày nay chúng ta luôn có sẵn ứng dụng Facebook trên điện thoại của mình. Khi bạn bắt gặp một khoảnh khắc nào đó và muốn chụp một bức hình để chia sẻ cho bạn bè cũng xem, bạn sẽ bấm vào biểu tượng máy ảnh trên Facebook và nó sẽ mở màn hình chụp ảnh cho bạn. Lúc này Facebook sẽ gọi API máy ảnh của điện thoại để sử dụng máy ảnh ngay trên ứng dụng mà không cần phải mở app chụp ảnh mặc định của điện thoại, và việc gọi API này thì không cần mạng. Ở một trường hợp khác, khi bạn vào xem thông tin một địa điểm nào đó trên Facebook thì sẽ thấy bản đồ chỉ đường tới địa điểm đó đúng không? Lúc đó Facebook sẽ gọi API (web services) từ Google Map để lấy thông tin bản đồ về và thao tác này chắc chắn cần mạng mới có thể làm được.
Cho tới hiện tại, việc tranh cãi SOAP hay RESTful tốt hơn vẫn chưa hề kết thúc. Tùy thuộc vào tính chất của dự án và sở thích của lập trình viên mà chúng ta sẽ lựa chọn chuẩn phù hợp. SOAP có thể phức tạp, phải tuân thủ nhiều quy tắc nhưng đôi khi nó lại dễ sử dụng trong một số trường hợp, còn đàn em của nó là RESTful nổi lên như một giải pháp thay thế mới mẻ song vẫn có những vấn đề của riêng nó.
Bài viết giới thiệu về API của mình đến đây là hết, mình rất vui vì một phần nào đó đã giúp các bạn có thêm những kiến thức mới. API theo chuẩn RESTful rất phổ biến, do đó kĩ năng kiểm thử API theo chuẩn này rất cần thiết với tester. Những bài viết tiếp theo mình sẽ giới thiệu cho các bạn về những công cụ thường được sử dụng trong việc test API như Postman, Charles,… Hẹn gặp lại các bạn lần sau!
Reference
- W3schools (no date) W3schools.com, W3Schools Online Web Tutorials. Available at: https://www.w3schools.com/xml/xml_soap.asp (Accessed: 04 October 2024).
- Jay (2023) Soap and rest at odds, The History of the Web. Available at: https://thehistoryoftheweb.com/soap-rest-odds/ (Accessed: 04 October 2024).
- Harrington, D. (2024) The history of rest apis – readme: Resource library, ReadMe. Available at: https://readme.com/resources/the-history-of-rest-apis (Accessed: 04 October 2024).
Author: Thang Tran