Atomic Design In Software Development
16/12/2024
964
Hello everyone! I’m Linh, a front-end developer passionate about discovering effective methods for system development. When I first entered the tech industry, I faced challenges organizing UI components logically and reusable. This experience motivated me to seek strategies to optimize my workflow while ensuring that the products I developed were easy to scale and maintain.
Recently, I explored the concept of Atomic Design, which has become a guiding principle for me in tackling these challenges more systematically and scientifically. This approach has significantly influenced my design thinking. Through this article, I aim to inspire you and offer a fresh perspective if you’re also looking for solutions for your systems.
Taking Cues From Chemistry
Looking for a way to build and create a design system reminds me of developments in other fields and industries. Many areas, such as design and architecture, have developed smart modular systems to produce incredibly complex things like airplanes, ships, and skyscrapers.
These thoughts take me back to my school days in chemistry labs. The idea is that all matter—whether solid, liquid, gas, simple, or complex—is made up of atoms. These atoms bond to form molecules, which combine into more complex organisms, eventually creating everything in our universe.
Similarly, systems built up from smaller components are more logical and connected. We can break the entire system into basic building blocks and work from there. That’s the core idea of atomic design.
What Is Atomic Design?
Atomic Design is an interface design methodology that focuses on creating a system of components rather than entire pages. Introduced by Brad Frost in 2013, this approach emphasizes using small, independent elements that can be reused and combined to form a cohesive whole. This strategy facilitates quicker product development, promotes a unified interface, and simplifies maintenance.
“Atomic Design is a methodology where designers prioritize creating individual components and then combine them, rather than designing entire pages.”
Atomic Design can enhance the design development process, promoting consistency, adaptability, and efficiency across projects. By applying the principles of Atomic Design, developers and designers can collaborate within a cohesive design system, ultimately delivering a scalable and high-quality user experience.
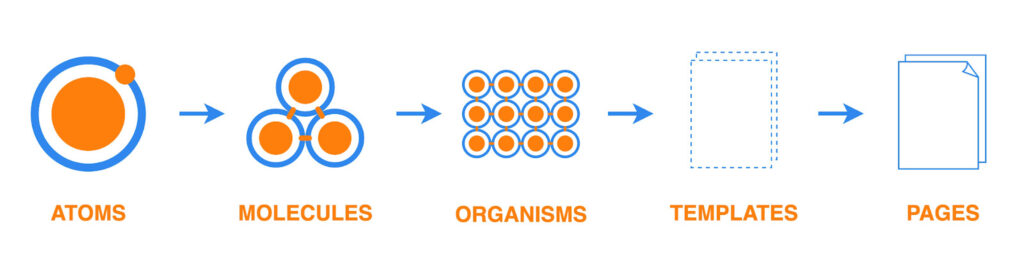
Atomic Design organizes components into five levels, progressing from simple to complex, as illustrated above:
- Atoms: These are the most basic components, such as HTML tags like buttons, inputs, labels, and icons.
- Molecules are combinations of two or more atoms that create more complex components. For example, a form group consists of an input and a label.
- Organisms are more complex UI components of multiple molecules and/or atoms. For instance, a form can comprise several form groups and buttons.
- Templates are layout frameworks created from organisms and molecules. They define how these components are arranged on a page but do not contain actual data or content; they represent an abstract structure.
- Pages: These are specific instances of templates where real content is added to create complete web pages or applications. Pages include all necessary components—atoms, molecules, organisms, and templates—along with specific content for end users to interact with.
In the following sections, we will explore each level of Atomic Design in detail.
Atoms
Similar to atoms in nature, these elements may seem abstract, but they are the foundational building blocks of all our user interfaces. In web interfaces, atoms are the fundamental HTML elements, such as labels, inputs, and buttons. As the smallest components, they cannot be broken down any further. Atoms can also be abstract concepts, including colors, fonts, and even more intangible UI aspects, like animations.

Molecules
When we combine atoms, things become more interesting and tangible. Molecules are groups of atoms that bond together and serve as the minor basic units of a compound. They possess unique properties and act as core elements within our design system.
For example, when atoms like labels, inputs, or buttons stand alone, they are useless. However, when combined into a form, they can work effectively together.
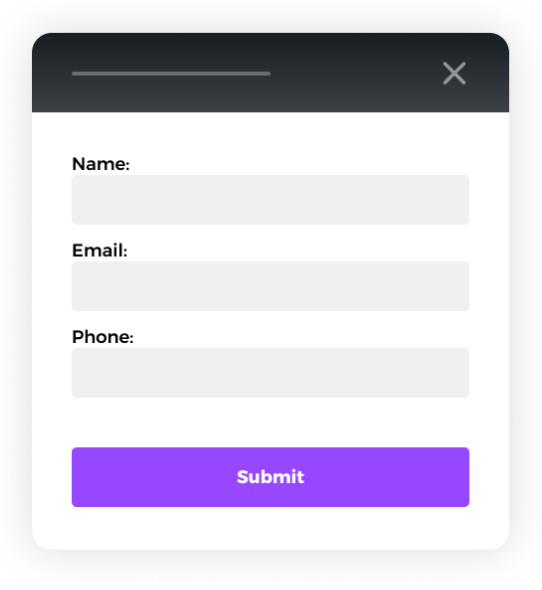
Molecules can be simple or complex and designed for reuse or one-time use. A molecule can have multiple variants (similar to components in a Variant in Figma) intended for different contexts or interactions (such as hover, pressing, or after a delay).
Organisms
Molecules provide us with building blocks to combine to create organisms. Organisms are groups of molecules that come together to form a more complex and complete structure.
Organisms can consist of similar or different elements. For instance, a website header might include a logo, menu, and search box. When you visit the category page of most e-commerce websites, you’ll see product listings displayed in a grid format, composed of smaller components like images, titles, captions, etc.
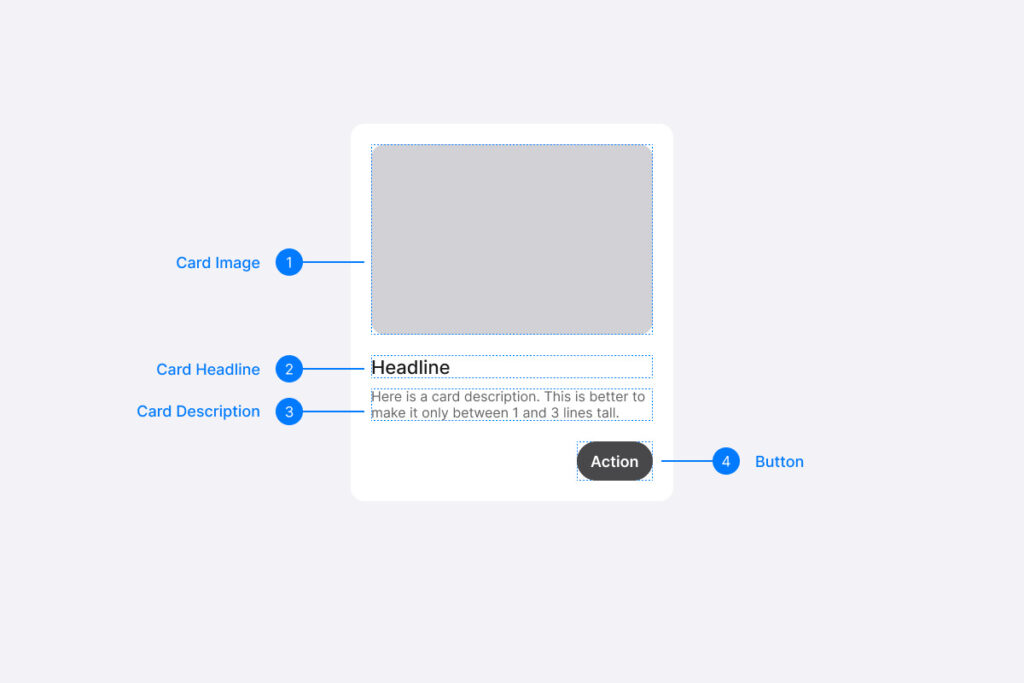
Templates
Templates are combinations of organisms that create complete pages. They focus on the basic content structure rather than the final content. Templates help clearly define important properties such as image sizes and text lengths, thereby establishing an effective system for managing dynamic content and ensuring alignment with the design.
“You can create good experiences without knowing the content. What you can’t do is create good experiences without knowing your content structure. What is your content made from, not what your content is?”

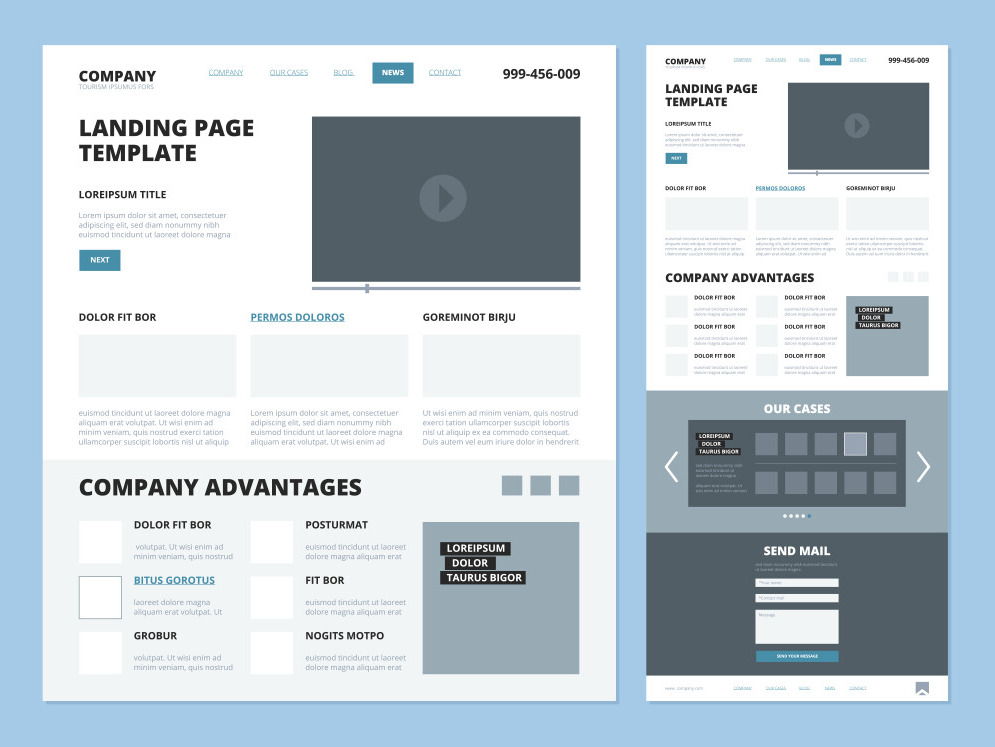
Pages
Pages are specific instances of templates. Placeholder content is replaced with representative content to depict what end users will see accurately. In simpler terms, pages are templates filled with real data for presentation purposes, offering the most realistic view of the design. Developers and designers will test how templates work with actual content, allowing designers to return and adjust to molecules, organisms, and templates as needed.
>>> Maybe you are interested:
- Differences In UX Demands Of A Desktop And Mobile App For A SaaS Product
- Top 10 Design Tools For UX And UI
- Top Emerging Trends In App UI Design
Benefits Of Applying Atomic Design In User Interface (UI) Design
Consistency
Atomic Design utilizes a modular approach, ensuring each interface element adheres to a consistent design language. When a component, such as a button or color, is modified or updated, these changes are automatically reflected across all pages, maintaining uniformity throughout the product. This consistency is crucial for large and complex design teams, where smooth and synchronized updates are essential.
Reusability
Reusability is one of the most significant advantages of Atomic Design. By defining basic components in a standardized way, you can reuse them throughout different contexts and parts of the product.
Due to this reusability, designers and developers can quickly integrate complex interfaces from standardized small components. For example, a button designed according to the standards can be used on various pages, from the homepage to product pages and forms, without needing to be recreated. This not only minimizes repetitive work but also ensures consistency across the entire design system.
Atomic Design’s reusability also promotes flexibility. It allows for easy updates or replacements of a component across the system without changing every detail on each page.
Maintainability
Atomic Design enables designers and developers to efficiently monitor and modify specific interface parts without impacting the entire system. The team can directly adjust the associated atoms or molecules when updates are required for a component, such as a button or color. These changes will automatically be reflected across all instances of that component. This approach reduces errors, minimizes repetitive tasks, and ensures that updates are consistently applied throughout the system.
Scalability
Like maintainability, Atomic Design allows designers and developers to expand the system by adding new components at the appropriate levels without disrupting the overall structure. For instance, if a new type of button or content combination is needed, the team can create new atoms or molecules and seamlessly integrate them into existing organisms and templates.
This method enables a system to quickly scale from a small application to larger, more complex products with many new pages and features while maintaining structural integrity. Atomic Design’s scalability ensures that products can evolve continuously and improve while minimizing the effort required for updates or adjustments to meet new demands. This helps products quickly adapt to changing user needs and market conditions.
A prime example of successfully implementing Atomic Design principles in UI design is the Shopee UI Design System. Shopee is building its interface systems based on Atomic Design principles to maintain consistency across its entire product range. By applying Atomic Design to fundamental components such as buttons, colors, and font families (Atoms), as well as groups of components like product lists (Molecules) and elements like navigation bars or product carousels (Organisms), Shopee enhances development speed through the reuse of standardized components, ensuring a consistent interface across multiple platforms.
Reality Use-Cases
Atomic Design is a robust methodology for creating user interfaces (UI) that has been extensively utilized in various open-source projects. Below are some notable systems that SupremeTech has adopted and incorporated into its client solutions:
Shopify Polaris Design System
Shopify uses Polaris to create a consistent interface for all applications related to Shopify. Similar to Shopee UI, Shopify Polaris applies the levels of Atoms, Molecules, and Organisms from Atomic Design into its design system. This helps Shopify enhance development efficiency and maintain long-term product quality.
MedusaJS
As an open-source e-commerce platform, MedusaJS implements atomic design to organize the UI components for its Storefront and Admin Dashboard.
Storefront UI: When building the Shopify Storefront interface for Medusa.js projects, Atomic Design helps organize UI components hierarchically.
1. Atoms:
- Button: Add to Cart button, View Product button.
- Text: Product title, price.
- Icon: Shopping cart icon, search icon.
2. Molecules:
- Product Card: Includes an image, title, price, and Add to Cart button.
- Navbar: Contains the logo, menu links, and search bar.
3. Organisms:
- Product Grid: A grid of product cards.
- Header: Combines the logo, navigation bar, and mini cart.
4. Templates: Product detail pages or product category pages.
5. Pages: Homepage, checkout page.
Admin Dashboard: Medusa.js also requires an admin UI to manage products, orders, and customers. Atomic Design helps organize the admin interface.
1. Atoms:
- Input: Input fields (product name, price).
- Button: Save, Delete, or Add product buttons.
- Badge: Displays order status (completed, processing).
2. Molecules:
- Search Bar: Search input field with a button and icon.
- Table Row: A row in a data table (product, order).
3. Organisms:
- Data Table: Displays a list of products or orders.
- Sidebar: Navigation menu for sections like Products and Orders.
4. Templates: Product list page with sidebar and data table.
5. Pages: Product management page, order management page.
By applying Atomic Design, MedusaJS achieves:
- Component reusability: UI components like buttons, forms, or cards can be reused in both the storefront and admin dashboard.
- Easy expansion: When adding new features (e.g., wishlist or promotional modules), you can combine existing Atoms, Molecules, and Organisms.
- Consistency assurance: Atomic Design ensures that components are uniformly designed from the admin interface to the storefront.
- Facilitated collaboration: Design and development teams can collaborate on a transparent hierarchical system.
Wrapping Up
Atomic Design is a valuable method in design and development; fundamentally, it serves as a framework for building user interfaces. The immediate benefits include time and cost savings, improved product consistency, enhanced team collaboration, support for accessibility efforts, and strategic long-term initiatives. These reasons drive organizations to adopt design systems. Mastering the core principles of modern design systems will help you grow as a designer or developer.