Back/Forward Cache, Hiện Đại Hay Hại Điện?
19/12/2022
733
Mục Lục
- Back/forward cache là gì?
- Nhận biết một trang được lưu, khôi phục từ back/forward cache.
- Tối ưu hóa cho back/forward cache bằng Chrome DevTools
- Những tác động của back/forward cache đối với trang web

Đã bao giờ bạn gặp trường hợp giống thế này chưa?
Bạn đang làm một website bán hàng. Khi người dùng đang ở trang thanh toán và đã điền đầy đủ thông tin tài khoản ngân hàng, tiếp theo họ chuyển đến trang giỏ hàng để cập nhật, sau đấy họ lại điều hướng trở lại trang thanh toán. Trên một số thiết bị, trang thanh toán sẽ được tải lại với form chứa thông tin tài khoản thanh toán được làm mới, nhưng trên một số thiết bị khác thì không, khi người dùng nhấp vào nút quay lại của trình duyệt, trang web trước đó sẽ không mất thời gian để tải lại mà nó sẽ xuất hiện ngay lập tức với những thông tin nhạy cảm mà người dùng đã nhập. Trên các thiết bị này, trang web đã được khôi phục từ một loại bộ nhớ đệm của trình duyệt có tên gọi là Back/forward cache. Trong vài trường hợp, việc lưu trữ nội dung của một trang web, để giúp người dùng có thể điều hướng trở lại ngay lập tức, mà không mất thời gian để tải lại như lúc ban đầu là một tính năng rất hay, hữu ích. Nhưng trong một số trường hợp khác, đấy cũng có thể trở thành bug.
Back/forward cache là gì?
Back/forward cache ( gọi tắt là bfcache) là một loại bộ nhớ đệm, giúp tối ưu hóa trình duyệt cho phép điều hướng quay lại và chuyển tiếp ngay lập tức. Nó cải thiện đáng kể trải nghiệm duyệt web cho người dùng — đặc biệt là những người có mạng hoặc thiết bị chậm hơn vì nó giúp trình duyệt có thể tải lại trang web trước đó mà không cần phải tải lại tài nguyên.
Phát hiện một trang được khôi phục từ bfcache.
Sự kiện pageshow được kích hoạt ngay sau sự kiện load khi trang web đang tải lần đầu và bất kỳ lúc nào trang được khôi phục từ bfcache. Sự kiện pageshow có một thuộc tính là persisted, nó sẽ có giá trị là true nếu trang được khôi phục từ bfcache (và ngược lại là false nếu không). Vì vậy, bạn có thể sử dụng thuộc tính persisted này để phân biệt trang được tải thông thường với trang được khôi phục từ bfcache. Ví dụ:
window.addEventListener('pageshow', (event) => {
if (event.persisted) {
console.log('Trang web nay duoc khoi phuc tu bfcache.');
} else {
console.log('Trang web nay duoc tai xuong binh thuong.');
}
});
Nhận biết một trang có thể được đưa vào bfcache
Ngược lại với sự kiện pageshow ta cũng có sự kiện pagehide. Sự kiện pagehide này sẽ được kích hoạt khi trang được tải xuống bình thường hoặc khi trình duyệt cố gắng đưa nó vào bộ nhớ đệm bfcache. Sự kiện pagehide này cũng có một thuộc tính là persisted. Nếu giá trị của nó là false thì bạn có thể chắc chắn rằng một trang sẽ không được đưa vào bfcache. Tuy nhiên, nếu giá trị của thuộc tính này là true, nó không đảm bảo rằng một trang chắc chắn sẽ được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm đâu nhé. Nó chỉ mang ý nghĩa là trình duyệt dự định lưu trang đấy vào bộ nhớ bfcache mà thôi, nhưng có thể có các yếu tố khiến nó không thể làm như vậy.
window.addEventListener('pagehide', (event) => {
if (event.persisted) {
console.log('Trang web nay *co the* duoc dua vao bfcache.');
} else {
console.log('Trang web nay khong duoc dua vao bfcache.');
}
});
Tối ưu hóa cho bfcache bằng Chrome DevTools
Bộ nhớ đệm bfcache đã có trên tất cả các trình duyệt web phổ biến hiện nay nhưng hiện chỉ có Chrome là có cung cấp cho chúng ta công cụ để kiểm tra mà thôi. Công cụ dành cho nhà phát triển của Chrome có thể giúp bạn kiểm tra các trang của mình để đảm bảo chúng được tối ưu hóa cho bfcache và xác định bất kỳ vấn đề nào có thể khiến chúng không đủ điều kiện.
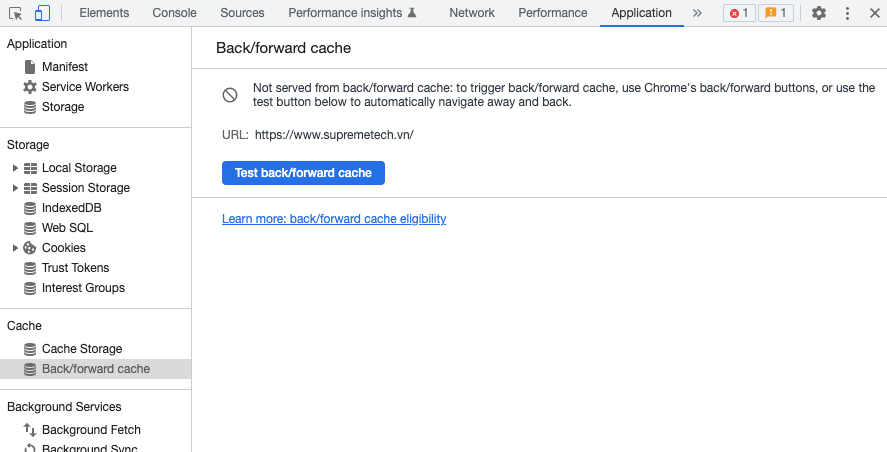
Để kiểm tra một trang cụ thể, hãy điều hướng đến trang đó trong Chrome và sau đó trong DevTools, đi tới Application > Back/forward cache. Tiếp theo, nhấp vào nút Run Test và DevTools sẽ cố gắng điều hướng và quay lại để xác định xem trang có thể được khôi phục từ bfcache hay không.
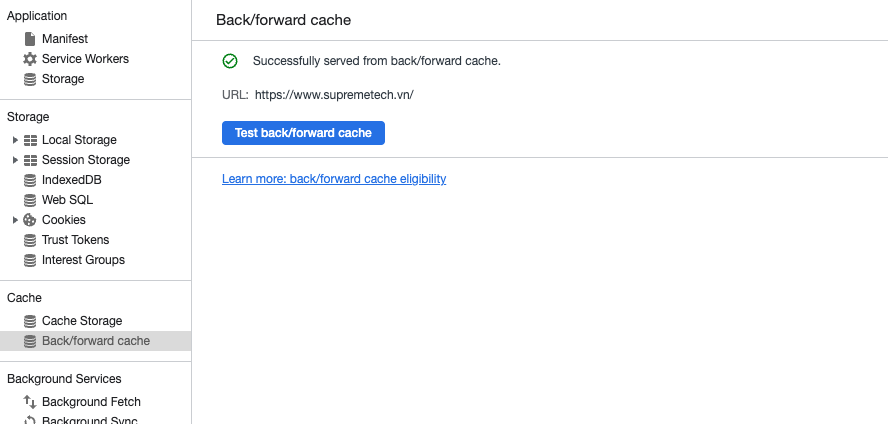
Nếu không thành công, bảng điều khiển sẽ cho biết trang không được khôi phục và liệt kê lý do tại sao. Nếu lý do là điều mà bạn với tư cách là nhà phát triển có thể giải quyết, thì lý do đó cũng sẽ được chỉ ra.
Cập nhật hoặc xóa dữ liệu sau khi trang web được khôi phục bfcache
Trở lại với vấn đề mà mình đặt ra ở đầu bài viết này. Nếu trang web của bạn lưu giữ trạng thái người dùng — đặc biệt là bất kỳ thông tin nhạy cảm nào của họ — thì dữ liệu đó cần được cập nhật hoặc xóa sau khi một trang được khôi phục từ bfcache.
Một ví dụ khác, thường gặp hơn là nếu người dùng đăng xuất khỏi trang web trên máy tính công cộng và người dùng tiếp theo nhấp vào nút quay lại. Điều này có thể làm lộ dữ liệu riêng tư mà người dùng cho rằng đã bị xóa sau khi họ đăng xuất. Để tránh những trường hợp như thế này, có một vài trick có thể ngăn trang được đưa vào bfcache nhưng vẫn sẽ có những ngoại lệ, vậy nên tốt hơn hết là bạn nên luôn cập nhật lại trang sau một sự kiện pageshow nếu như event.persisted có giá trị là true.
Đoạn mã sau sẽ kiểm tra sự hiện diện của cookie dành riêng cho trang web trong sự kiện pageshow và tải lại nếu không tìm thấy cookie:
window.addEventListener('pageshow', (event) => {
if (event.persisted && !document.cookie.match(/my-cookie/)) {
// Bat buoc tai lai trang neu nhu nuoi dung da dang xuat.
location.reload();
}
});
Thống kê lượt truy cập trang web có sử dụng bfcache
Như đã giới thiệu ở phần trên, nếu một trang web được khôi phục từ bfcache thì nó sẽ không tốn tài nguyên, dữ liệu mạng, điều đó cũng đồng nghĩa với việc trang web đó đã bị mất đi một lượt truy cập nếu bạn theo dõi lượt truy cập vào trang web của mình bằng các công cụ phân tích vì hầu hết các thư viện công cụ phân tích phổ biến không theo dõi khôi phục bfcache dưới dạng số lần xem trang mới. Vậy nên, nếu bạn không biết/lường được vấn đề này thì việc giảm lưu lượng truy cập, lượt xem do bfcache gây ra sẽ ít nhiều có ảnh hưởng không tốt đến việc xếp hạng trang web của bạn, mặc dù nó giúp tăng trải nghiệm của người dùng.
Nếu bạn không muốn số lần xem trang của mình giảm xuống do trình duyệt bật bfcache, bạn có thể báo cáo số lần khôi phục bfcache dưới dạng số lần xem trang (được khuyến nghị) bằng cách lắng nghe sự kiện pageshow và kiểm tra thuộc tính persisted.
Ví dụ sau đây cho thấy cách thực hiện việc này với Google Analytics ( logic cũng tương tự đối với các công cụ phân tích khác ) :
// Gui mot luot xem khi trang duoc tai lan dau tien.
gtag('event', 'page_view');
window.addEventListener('pageshow', (event) => {
// Gui mot luot xem khi trang duoc khoi phuc tu bfcache.
if (event.persisted) {
gtag('event', 'page_view');
}
});
Tổng kết
Cái gì cũng có giá trị của nó, cũng có tồn tại những ưu và nhược điểm, bfcache cũng không ngoại lệ. Việc quay lại một trang trước đó mà không phải tải lại từ đầu là một tính năng rất hữu ích, không chỉ giúp tăng tốc độ điều hướng mà còn giảm việc sử dụng dữ liệu, vì trình duyệt không cần phải tải lại tài nguyên. Điều này giúp tăng trải nghiệm của người dùng đáng kể nhưng nó cũng tiềm ẩn rủi ro về bảo mật dữ liệu cá nhân, làm giảm lượt truy cập trang trực tuyến và một số vấn đề khác nữa. Điều quan trọng là bản thân người lập trình viên phải biết và kiểm soát được nó trong từng trường hợp, vì nếu không, trong một số trường hợp, tính năng cũng có thể sẽ trở thành bug.
Bài viết này không chỉ dành cho các lập trình viên tham khảo mà ngay cả các tester cũng có thể đưa vào trong test case của mình đặc biệt là trong các trang web có yêu cầu yếu tố bảo mật hoặc những trang có dữ liệu thường xuyên thay đổi.
Hi vọng bài viết này của mình hữu ích đối với các bạn. Đừng quên share và gắn bookmark cho bài viết này để tiện xem lại sau này nhé 😉 !
Tài liệu tham khảo
Related Blog